acetabular labral tear tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology : OEM Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears. Learn about the three types of steam sterilization cycles: gravity, prevacuum and steam flush pressure pulse (SFPP). SFPP is a dynamic air removal cycle that co.
{plog:ftitle_list}
VistaCool - the only direct-to-drain system designed from the ground up for your STATIM ® .
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.
Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. It serves as a gasket between the acetabulum and head of the femur, creating a vacuum seal and providing stability between the bones.
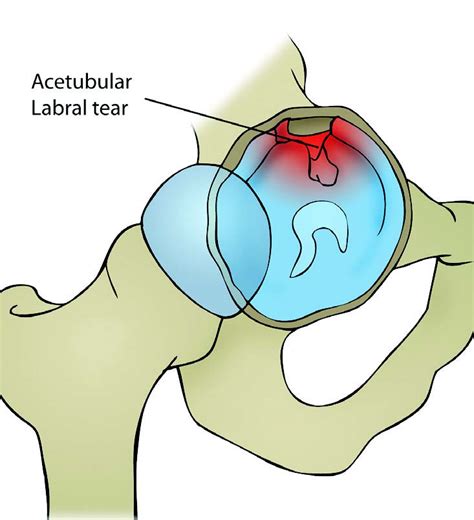
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems. This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single test has been identified as having a significant positive predictive value in .
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. It serves as a gasket between the acetabulum and head of the femur, creating a vacuum seal and providing stability between the bones. Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic. Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
describe autoclaving process
Additionally, the duration of the sterilization process depends on the temperature and pressure settings, with a minimum of 30 minutes required at 250°F (121°C) and 20 psi. By subjecting the materials to these conditions, .Like other sterilization systems, the steam cycle is monitored by mechanical, chemical, and biological monitors. Steam sterilizers usually are monitored using a printout (or graphically) by measuring temperature, the time at the temperature, and pressure.
acetabular labral tear tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology